
● EXPLAINED INTERMITTENT FASTING:-
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a popular approach to weight loss that involves alternating periods of eating and fasting.By restricting eating windows and extending fasting periods, IF promotes significant weight reduction by targeting multiple physiological pathways. During fasting, insulin levels drop, and the body shifts from relying on glucose to burning stored fat for energy, resulting in increased lipolysis and fat oxidation. Additionally, IF reduces inflammation, improves insulin sensitivity, and enhances human growth hormone (HGH) production, all of which contribute to enhanced fat burning and weight loss.https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/intermittent-fasting-what-is-it-and-how-does-it-work

● BENEFITS IN ALL AREAS:-
• Benefits:-
1. Weight Loss: Reduced calorie intake, increased fat burning.
2. Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Reduced risk of type 2 diabetes.
3. Increased Human Growth Hormone (HGH): Improved muscle mass, bone density.
4. Enhanced Autophagy: Cellular renewal, reduced inflammation.
5. Improved Mental Clarity: Increased focus, concentration.
6. Reduced Inflammation: Improved overall health.
7. Increased Longevity: Reduced oxidative stress.

• Physical benefits:-
1. Weight Loss: Reduced body weight and body fat.
2. Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Reduced risk of type 2 diabetes.
3. Enhanced Fat Burning: Increased lipolysis and fat oxidation.
4. Reduced Inflammation: Improved overall health.
5. Improved Cardiovascular Health: Reduced blood pressure and cholesterol.
6. Increased Human Growth Hormone (HGH): Improved muscle mass and bone density.
7. Improved Cellular Cleaning: Autophagy and reduced oxidative stress.
• Mental and Emotional Benefits:-
1.Improved mental clarity: Increased focus and concentration.
2. Reduced Stress and Anxiety: Improved resilience.
3. Improved Mood: Reduced symptoms of depression.
4. Increased Energy: Improved physical and mental performance.
5. Improved Sleep Quality: Better rest and recovery.
• Longevity and Anti-Aging Benefits:-
1. Telomere Length: Increased telomere length, improved cellular aging.
2. Reduced Oxidative Stress: Improved cellular health.
3. Improved Epigenetics: Reduced disease risk.
4. Increased Cellular Renewal: Autophagy and improved tissue health.
• Additional Benefits:-
1. Improved Immune Function: Reduced inflammation.
2. Reduced Cancer Risk: Improved cellular health.
3. Improved Bone Health: Increased bone density.
4. Improved Skin Health: Reduced wrinkles and improved complexion.
5. Increased Productivity: Improved focus and energy.
● Potential Benefits for Specific Health Conditions:-
1. Type 2 Diabetes
2. Obesity
3. Cardiovascular Disease
4. Cancer
5. Neurodegenerative Diseases (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s)
6. Autoimmune Diseases (Multiple Sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis)
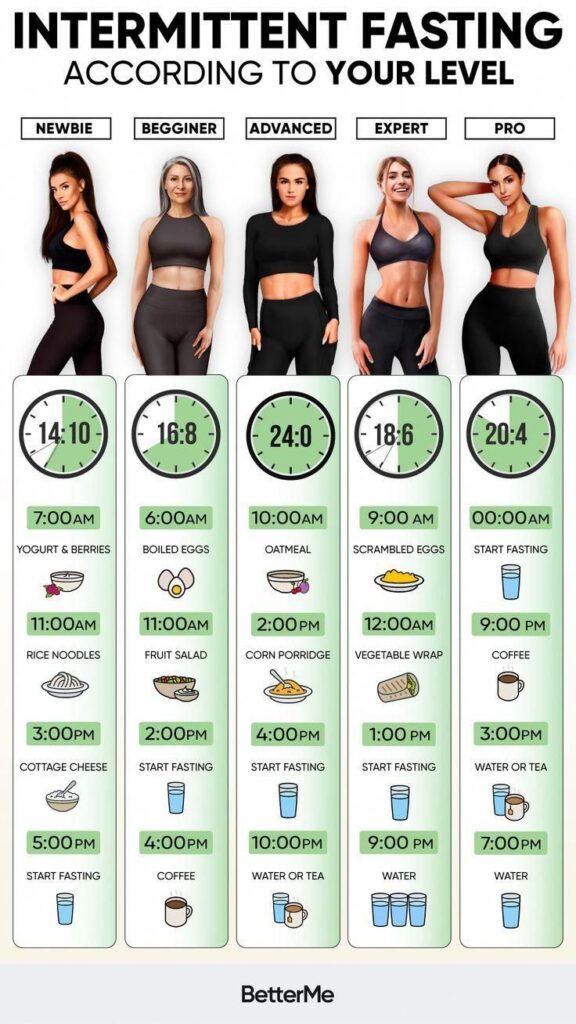
● Types of Intermittent Fasting:-
1. 16:8 Method: Fast for 16 hours, eat within 8-hour window.
2. 5:2 Diet: Eat normally for 5 days, restrict calories to 500-600 on other 2 days.
3. Alternate Day Fasting: Alternate between days of normal eating and days of calorie restriction.
4. Eat-Stop-Eat: Fast for 24 hours once or twice a week.
5. Warrior Diet: Eat only fruits and vegetables during the day, eat a large meal at night.
6. 12-Hour Window: Limit eating to 12-hour window each day.
● Tips for Success:-
1. Start slowly (12-hour fasting window).
2. Listen to your body (adjust fasting schedule as needed).
3. Stay hydrated.
4. Eat nutrient-dense foods during eating window.
5. Avoid excessive exercise during fasting periods.
6. Be consistent.
7. Monitor progress (track weight, measurements, blood work).
● Common Side Effects:-
1. Hunger and cravings.
2. Fatigue.
3. Headaches.
4. Nausea.
5. Constipation.
6. Irritability.
7. Dizziness.
● Foods to Eat During Eating Window:-
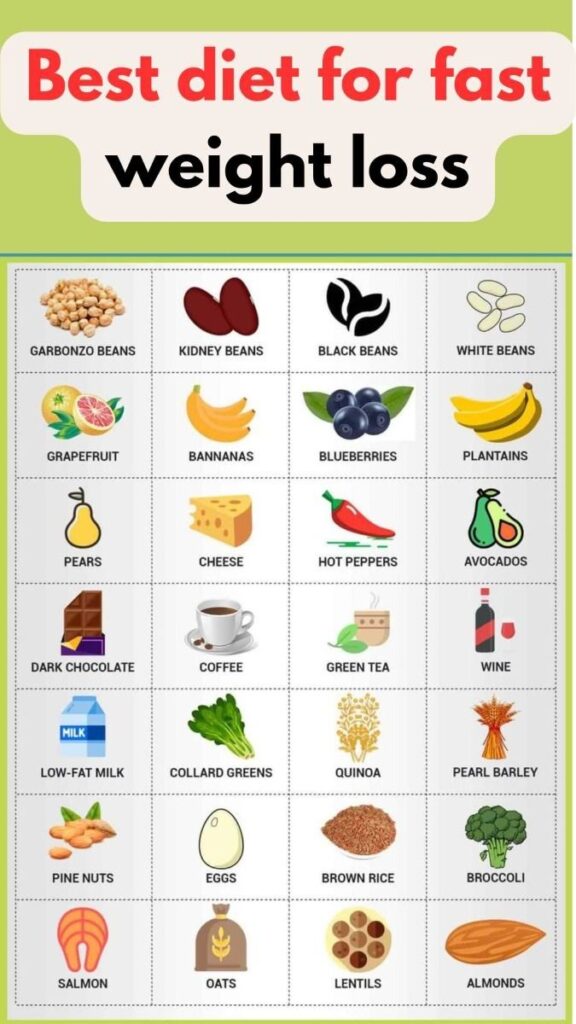
1. Protein-rich foods (meat, fish, eggs).
2. Vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, bell peppers).
3. Fruits (berries, citrus fruits, apples).
4. Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat).
5. Healthy fats (avocado, nuts, seeds).

● Foods to Avoid:-
1. Sugary drinks.
2. Refined carbohydrates.
3. Processed meats.
4. Fried foods.
5. High-sodium foods.
● Intermittent Fasting and Exercises:-
1. Best exercises during fasting: yoga, walking, light cardio.
2. Avoid intense exercise during fasting.
3. Stay hydrated during exercise.
4. Listen to your body (adjust exercise schedule as needed).
● Intermittent Fasting and Health Conditions:-
1.Diabetes: Consult a healthcare professional.
2. Low blood Pressure: Consult a healthcare professional.
3. Pregnancy breastfeeding: Avoid intermittent fasting.
4. Eating disorder: Avoid intermittent fasting.
● How Intermittent Fasting Works for Weight Loss:-
1. Reduced calorie intake
2. Increased fat oxidation
3. Improved hormone regulation (insulin, leptin, ghrelin)
4. Enhanced cellular cleaning (autophagy)
5. Reduced inflammation
● Tips for Successful Intermittent Fasting:-
1. Start slowly (12-hour fasting window)
2. Listen to your body (adjust fasting schedule as needed)
3. Stay hydrated.
4. Eat nutrient-dense foods during eating window.
5. Avoid excessive exercise during fasting periods.
6. Be consistent.

● Common Side Effects:-
1. Hunger and cravings
2. Fatigue
3. Headaches
4. Nausea
5. Constipation
● Who Should Not Try Intermittent Fasting:-
1. Pregnant or breastfeeding women
2. Children and teenagers
3. People with a history of eating disorders
4. Those with certain medical conditions (diabetes, low blood pressure)
5. Older adults (consult a healthcare professional)
● Intermittent Fasting and Hormones:-
1. Insulin: Reduced insulin resistance, improved glucose regulation
.2. Leptin: Increased leptin sensitivity, improved weight regulation.
3. Ghrelin: Reduced ghrelin levels, improved appetite regulation.
4. Cortisol: Reduced cortisol levels, improved stress management.
5. Adiponectin: Increased adiponectin levels, improved insulin sensitivity.
● Intermittent Fasting and Cellular Health:-
1. Autophagy: Enhanced cellular renewal, reduced inflammation.
2. Mitochondrial function: Improved energy production, reduced oxidative stress.
3. Telomere length: Increased telomere length, improved cellular aging.
4. Epigenetics: Improved gene expression, reduced disease risk.
● Intermittent Fasting and Mental Health:-
1. Reduced stress and anxiety
2. Improved mood and cognitive function
3. Increased focus and concentration
4. Reduced symptoms of depression
● Intermittent Fasting and Athletic Performance:-
1. Improved endurance and stamina
2. Increased human growth hormone (HGH) production
3. Enhanced muscle recovery and growth
4. Improved mental clarity and focus
● Intermittent Fasting and Women’s Health:-
1. Improved menstrual regularity
2. Reduced symptoms of PMS
3. Improved fertility
4. Reduced risk of breast cancer
● Intermittent Fasting and Aging:-
1. Reduced oxidative stress
2. Improved cellular renewal
3. Increased telomere length
4. Reduced risk of age-related diseases
● Common Intermittent Fasting Mistakes:-
1. Not listening to your body
2. Inconsistent fasting schedule
3. Poor hydration
4. Lack of nutrient-dense foods
5. Excessive exercise during fasting
● Intermittent Fasting and Medications:-
1. Consult a healthcare professional before starting IF
2. Monitor blood sugar levels (diabetes)
3. Monitor blood pressure (hypertension)
4. Adjust medication dosages as needed.
● Physiological Effects:-
1. Insulin Sensitivity: IF improves insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels.
2. Autophagy: IF stimulates autophagy, cellular renewal, and waste removal.
3. Hormone Regulation: IF affects hormone production, including insulin, leptin, ghrelin, and cortisol.
4. Inflammation Reduction: IF reduces inflammation, improving overall health.
● Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms:-
1. mTOR Pathway: IF inhibits mTOR, promoting cellular renewal and reducing cancer risk.
2. AMPK Activation: IF activates AMPK, improving energy metabolism and reducing inflammation.
3. SIRT1 Activation: IF activates SIRT1, promoting cellular longevity and stress resistance.
4. Telomere Length: IF increases telomere length, improving cellular aging.
● Neurological and Psychological Effects:-
1. Neuroplasticity: IF promotes neuroplasticity, improving cognitive function.
2. Stress Resistance: IF increases stress resistance, reducing anxiety and depression.
3. Mood Regulation: IF regulates mood, reducing symptoms of depression.
4. Cognitive Function: IF improves cognitive function, including focus and concentration.
● Benefits for Specific Health Conditions:-
1. Type 2 Diabetes: IF improves insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels.
2. Obesity: IF promotes weight loss, improving body composition.
3. Cardiovascular Disease: IF reduces inflammation, improving cardiovascular health.
4. Cancer: IF inhibits cancer cell growth, improving treatment outcomes.
● Potential Risks and Considerations:-
1. Malnutrition: IF can lead to malnutrition if not planned properly.
2. Dehydration: IF can cause dehydration if not enough fluids are consumed.
3. Hypoglycemia: IF can cause hypoglycemia in individuals with diabetes.
4. Adverse Effects on Reproductive Health: IF may affect reproductive health in certain.
● Nutritional Considerations:-
1. Macronutrient Balance: Ensuring adequate protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
2. Micronutrient Intake: Ensuring adequate vitamins and minerals.
3. Hydration: Drinking enough water during fasting periods.
4. Electrolyte Balance: Maintaining electrolyte balance during fasting.
click herehttps://khansasaadhassan.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=176&action=edit


1 thought on “Explained Intermittent Fasting: Benefits, How does it work?”